Spinach heart, the age of frankenstein is here
- unpadhimbio
- Nov 25, 2020
- 2 min read
Vegetables are good for your health, but now there's a whole new way that one veggie could help your heart: Spinach leaves can be used as a scaffold for beating human heart cells, a new study finds. In several experiments, scientists grew beating human heart cells on spinach leaves by perfusing them with a detergent solution, which stripped them of their plant cells. This proof-of-concept study suggests that multiple spinach leaves could be used to grow layers of healthy heart muscle that could one day be used to treat heart attack patients, the researchers said.
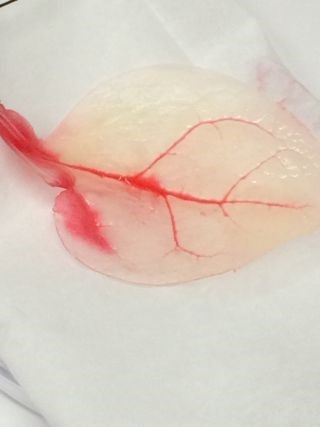
"We have a lot more work to do, but so far this is very promising,” Glenn Gaudette, the study's senior researcher and a professor of biomedical engineering at the Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Worcester, Massachusetts, said in a statement. "Adapting abundant plants that farmers have been cultivating for thousands of years for use in tissue engineering could solve a host of problems limiting the field."
In addition, the researchers said they think they could deliver blood and oxygen to developing tissues by pouring fluids through the spinach leaves' veins. "When I looked at the spinach leaf, its stem reminded me of an aorta," said Joshua Gershlak, a graduate student of biomedical engineering at WPI and the study's lead researcher. "So I thought, let’s perfuse [the fluids] right through the stem." Spinach leaves make a good scaffold because once the plant cells are washed away, a cellulose structure remains, the researchers said. "Cellulose is biocompatible has been used in a wide variety of regenerative medicine applications, such as cartilage tissue engineering, bone tissue engineering and wound healing," the researchers wrote in the study.
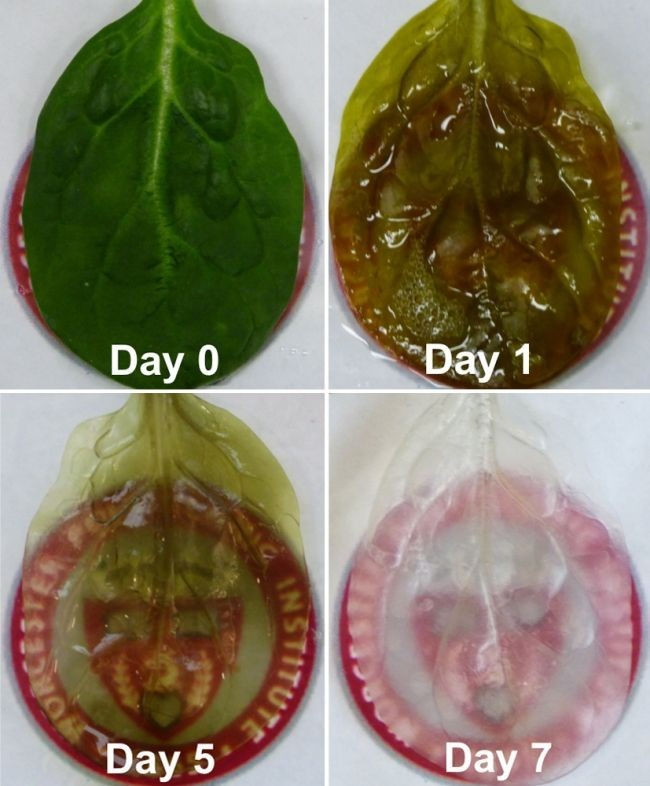
In addition to spinach leaves, the researchers also removed plant cells from parsley, Artemesia annua (sweet wormwood) and peanut hairy roots. Scaffolds from these plants, and perhaps others, could be helpful for other types of specialized tissue regeneration, they said.
Although spinach leaves have many veins, making them a well-suited scaffold for heart tissue, other plans show promise for other medical uses. Namely, the "cylindrical, hollow structure of the stem" of the jewelweed plant could be used as a graft for an artery, they said. In addition, wood from trees "might be useful in bone engineering," due in part to its strength, they wrote.
Plants such as these may provide economic and environmental advantages to the biomedical field. "By exploiting the benign chemistry of plant tissue scaffolds, we could address the many limitations and high costs of synthetic, complex composite materials," the researchers wrote. Plants are easy to grow and are environmentally friendly. However, it remains to be seen whether these spinach scaffolds are safe for human use, and whether some people might have an immune response to tissues grown on plant scaffolds.
Laura Geggle

Comments